Understand the Question
Why are racing bikes and everyday bikes so different?
Leading Question:
In daily cycling, we usually sit straight while cycling because we feel most comfortable in this position.

However, have you wondered why professional cyclists on TV bend down so much while they are cycling? What incentivices them to do so?
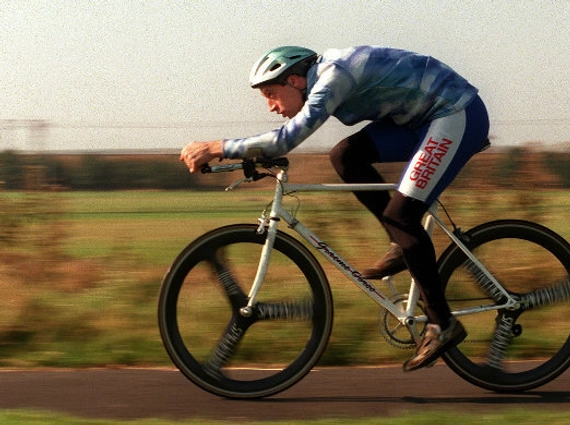

Moreover, have you wondered why racing bikes look so different compared to bikes we ride everyday?
This site will investigate the reasons behind these questions, and explain them to you.
Why professional cyclist bend down so much?
It is easy to explain the first part of the problem: In everyday life, we choose to sit straight while biking because it feels more comfortable. (duh)
Now, the only question left unsolved becomes: Why professional cyclists bend down so much? What benefit can this bring to them?
The answer is: Air resistance (drag).
Newton's First Law
According to Newton's first law (also known as the law of inertia), an object will remain at rest or move in constant motion unless acted upon by an external force.
This means, under an ideal situation (vacuum), objects like bikes will move towards a certain direction forever once you step on the pedal once-you dont even need to continue adding force on the bike. It will keep moving without slowing down.
However, we all know this isn't the case, because we have to constantly step the pedal to keep moving, and if we dont add force like this, the bike will decellerate and stop.
Using the law of intertia, it is not difficult to make the conclusion that there is an external force acting on the bike that slows it down on Earth. What is it?
It is mainly Air Resistance.
Air resistance is the force in the air that acts against the motion of a moving object like a bike.
Explaining Air Resistance
To us, air feels like its invisible and empty. In reality, however, air is made up of bzillions of tiny particles. These particles collide with each other in the air because of random movement. When an object move, the particles in air will collide with the object, creating a force that opposes the motion of the object.
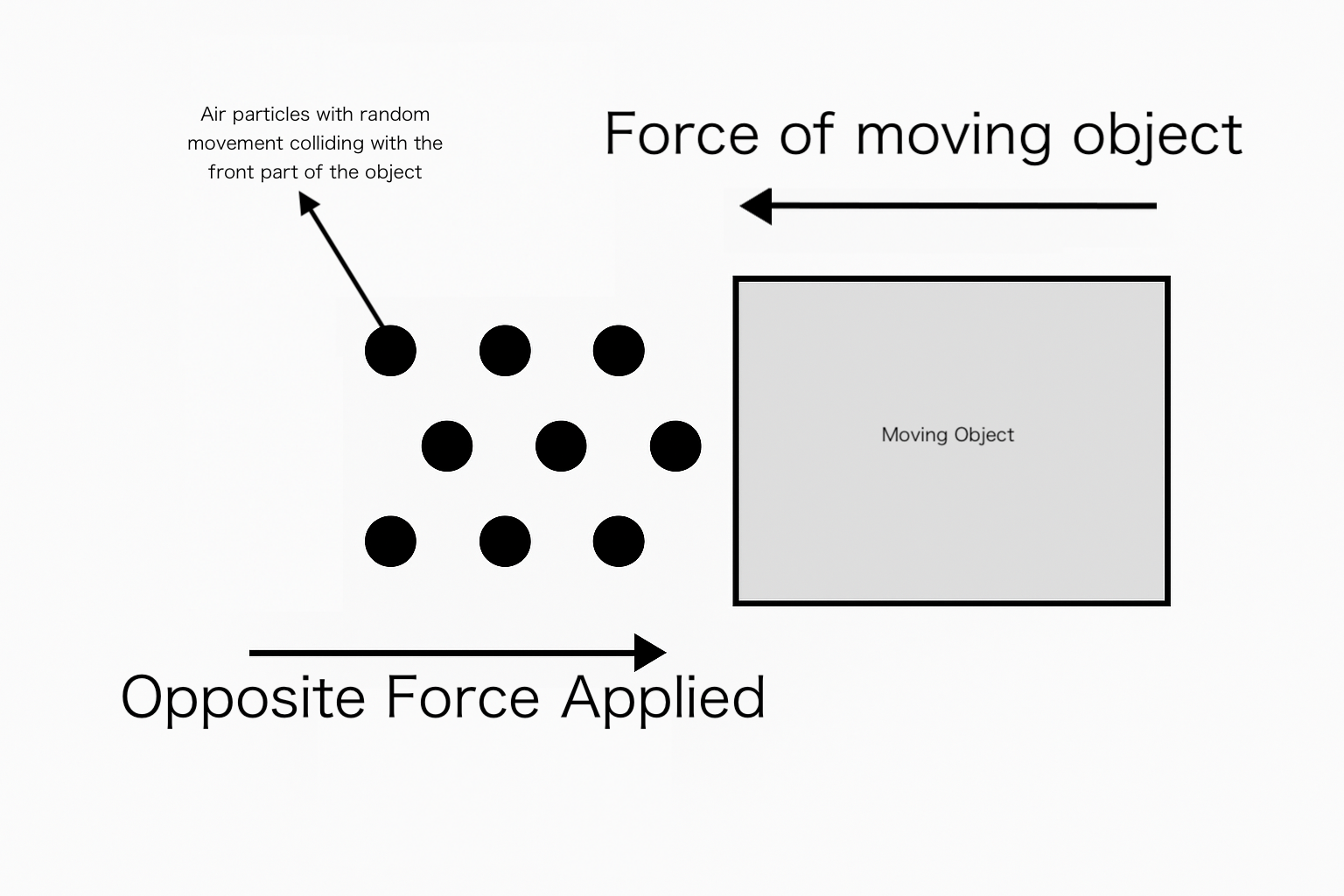
When a cyclist is riding a bike, the air resistance acts against the motion of the bike, making it harder for the cyclist to pedal and maintain speed. The faster the cyclist goes, the greater the air resistance becomes. This is because as speed increases, more air particles collide with the cyclist and bike per unit of time, resulting in a stronger opposing force.
Cyclists want to go as fast as they can, so they want to reduce air resistance as much as possible, so their energy is most efficiently used. Therefore, they will bend down to reduce their frontial area (the area directly facing the air), so that the air resistance is decreased, and cyclists get to go faster with the same amount of force applied to the bike.
Why can cyclists reduce air resistance via bending down?
Cyclists reduce air resistance through bending down because The smaller the area that touches wind particles in front, the less air resistance. This is true because when particles apply resistive forces to the moving object, they bounce off the object to apply the opposite force. Therefore, the bigger the area the moving object is facing the wind, more particles will collide, creating a larger resistive force, therefore increasing air resistance. Professional cyclists wish the exact opposite to happen-to decrease air resistance, therefore they bend down to reduce the frontal area.
Further explaination and experiments will be conducted on the next page.
Learn more about Air Resistance on the next page ->


